New study shows how spectroscopic and isotopic techniques can be combined to better understand the dynamics of phosphorus cycling in soils
Paper published by Julian Helfenstein, Federica Tamburini, Christian von Sperber, Michael S. Massey, Chiara Pistocchi, Oliver A. Chadwick, Peter M. Vitousek, Ruben Kretzschmar, and Emmanuel Frossard in Nature Communications.
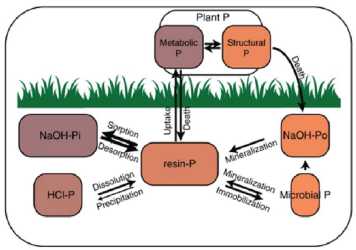
Current understanding of phosphorus (P) cycling in soils can be enhanced by integrating previously discrete findings concerning P speciation, exchange kinetics, and the underlying biological and geochemical processes. Here, we combine sequential extraction with P K-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy and isotopic methods (33P and 18O in phosphate) to characterize P cycling on a climatic gradient in Hawaii. We link P pools to P species and estimate the turnover times for commonly considered P pools. Dissolved P turned over in seconds, resin-extractable P in minutes, NaOH-extractable inorganic P in weeks to months, and HCl-extractable P in years to millennia. Furthermore, we show that in arid-zone soils, some primary mineral P remains even after 150 ky of soil development, whereas in humid-zone soils of the same age, all P in all pools has been biologically cycled. The integrative information we provide makes possible a more dynamic, process-oriented conceptual model of P cycling in soils. external page https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-018-05731-2