New publication studies the structural effects of Al and Fe occupancy in jarosite and alunite.
The new article, published in ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, explores how to use a range of laboratory-based mineral characterisation techniques to reveal the elemental substitution of jarosite. The results have implications for measuring the Al content in natural samples of jarosite.
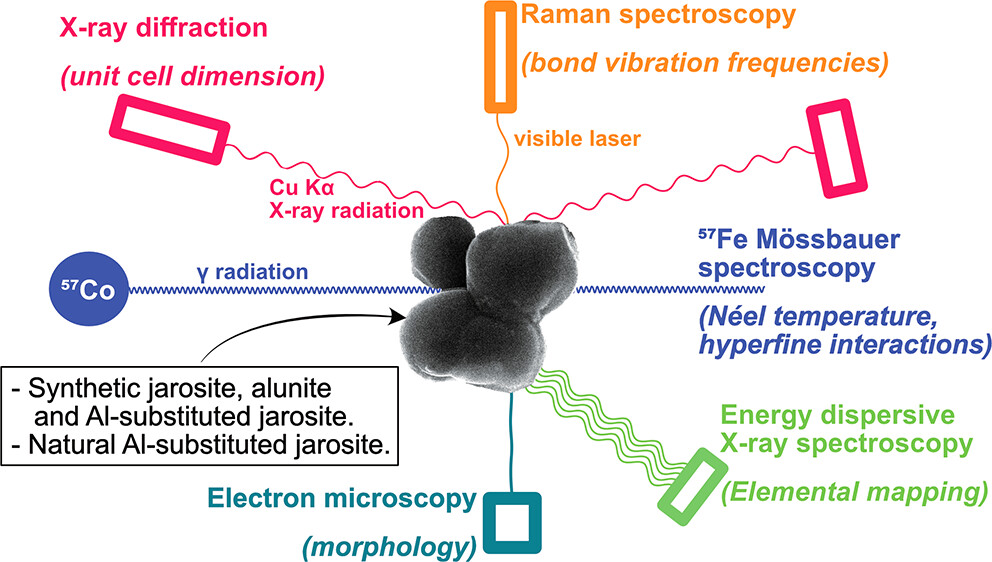
The alunite supergroup of minerals contains several hydroxysulfate mineral phases that commonly occur in acidic natural and engineered environments. The main division of the mineral supergroup defines two minerals, jarosite and alunite, based on the relative structural occupancy by Al or Fe, respectively. However, intermediate members of the jarosite-alunite solid solution have not been extensively characterized, especially in the environment. Here, we link the mineral unit cell sizes measured by X-ray diffraction, peak shifts in Raman spectra, fitting parameters in Mössbauer spectroscopy, and elemental quantification by EDX spectroscopy to known amounts of Al substitution in two synthetic series of Al-substituted jarosite (up to Al-for-Fe substitution of 9.5%) and unknown Al substitution in a natural jarosite isolated from an acid sulfate soil. Strong correlations were observed between the Al substitution of the jarosite samples and unit cell size, position of several vibrational peaks in Raman spectroscopy, and the temperature of magnetic ordering. In addition, elemental mapping provided a robust way to characterize the Al content of jarosite. As the techniques were effective in quantifying the Al or Fe content of jarosite-alunite supergroup mineral samples, without the need for sample dissolution, the findings support the application of these spectroscopy techniques to characterize natural jarosite-alunite samples. Using these techniques, we demonstrate at least 5% Al-for-Fe substitution in a jarosite sample from an acid sulfate soil. Application to environmental samples is especially useful in cases where it is otherwise difficult to directly measure the Al content of a mineral sample or when Al-for-Fe substitution influences the spectral responses to substitution at other sites in the crystal structure.
The external page full text is available online.