Ferrous Iron Enhances Arsenic Sorption and Oxidation by Non-stoichiometric Magnetite and Maghemite
Reto Gubler (MSc 2019) and Laurel ThomasArrigo have published a paper looking at arsenic speciation and mobility during interactions with non-stoichiometric magnetite and ferrous iron in the Journal of Hazardous Materials.
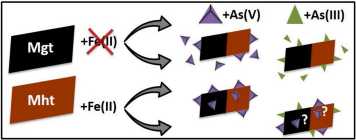
Arsenic-contaminated waters affect millions of people on a daily basis. Because the toxicity of As is dependent on the redox state, understanding As biogeochemistry, particularly in reducing environments, is critical to addressing the environmental risk that As poses. Sorption of As to Fe(III)-(oxyhydr)oxides is an important mechanism for As removal from solution under anoxic conditions. However, dissolved ferrous Fe (Fe(II)) also occurs under anoxic conditions, and the impact that Fe(II)-catalyzed recrystallization of crystalline Fe minerals has on As sorption mechanisms is not clear. Our research investigates the potential for non-stoichiometric magnetite, a commonly occurring mixed-valence Fe oxide in anoxic aquifers, to adsorb and/or incorporate inorganic As species during Fe(II)-catalyzed recrystallization at neutral pH, with particular focus on the impact of mineral stoichiometry (Fe(II):Fe(III) = 0.23 and 0.0) and varying Fe(II) concentrations. By following aqueous As concentrations and speciation over time coupled with As K-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy, our results demonstrate that the presence of Fe(II) substantially enhanced As removal from solution. In addition, we highlight a Fe(II)-induced mechanism through which highly mobile, toxic As(III) species are oxidized on the mineral surface to form As(V). Furthermore, the presence of Fe(II) promotes the structural incorporation of As(V) into the non-stoichiometric magnetite and maghemite structures. These results highlight the potential of Fe(II)-reacted non-stoichiometric magnetite or maghemite as pathways for long-term As sequestration in anoxic environments.