A new study about the the influence of soil properties and temperature on the reductive solubilization of arsenic in a mining-impacted river floodplain
Publication of Michael Simmler, Jérôme Bommer, Sarah Frischknecht, Iso Christl, Tsvetan Kotsev and Ruben Kretzschmar in Environmental Pollution.
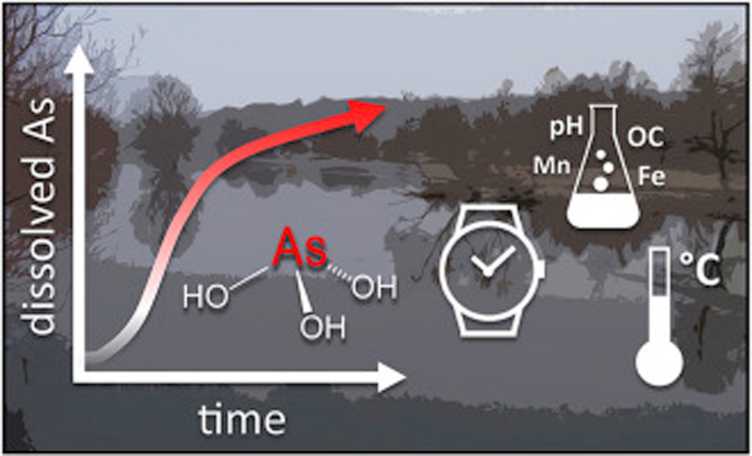
Mining activities have contaminated many riverine floodplains with arsenic (As). When floodplain soils become anoxic under water-saturated conditions, As can be released from the solid phase. Several microbially-driven As solubilization processes and numerous influential factors were recognized in the past. However, the interplay and relative importance of soil properties and the influence of environmental factors such as temperature remain poorly understood, especially considering the (co)variation of soil properties in a floodplain. We conducted anoxic microcosm experiments at 10, 17.5, and 25 °C using 65 representative soils from the mining-impacted Ogosta River floodplain in Bulgaria. To investigate the processes of As solubilization and its quantitative variation we followed the As and Fe redox dynamics in the solid and the dissolved phase and monitored a range of other solution parameters including pH, Eh, dissolved organic C, and dissolved Mn. We related soil properties to dissolved As observed after 20 days of microcosm incubation to identify key soil properties for As solubilization. Our results evidenced reductive dissolution of As-bearing Fe(III)-oxyhydroxides as the main cause for high solubilization. The availability of nutrients, most likely organic C as the source of energy for microorganisms, was found to limit this process. Following the vertical nutrient gradient common in vegetated soil, we observed several hundred μM dissolved As after 1–2 weeks for some topsoils (0–20 cm), while for subsoils (20–40 cm) with comparable total As levels only minor solubilization was observed. While high Mn contents were found to inhibit As solubilization, the opposite applied for higher temperature (Q10 2.3–6.1 for range 10–25 °C). Our results suggest that flooding of nutrient-rich surface layers might be more problematic than water-saturation of nutrient-poor subsoil layers, especially in summer floodings when soil temperature is higher than in winter or spring.
external page http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0269749117314045